React Hooks原理
背景介绍
如果没有Hooks,在函数式组件中,只能接受Props、渲染UI、触发事件等。状态无法保存、逻辑也无法复用。所以Hooks的作用就是复用逻辑和保存状态。
流程
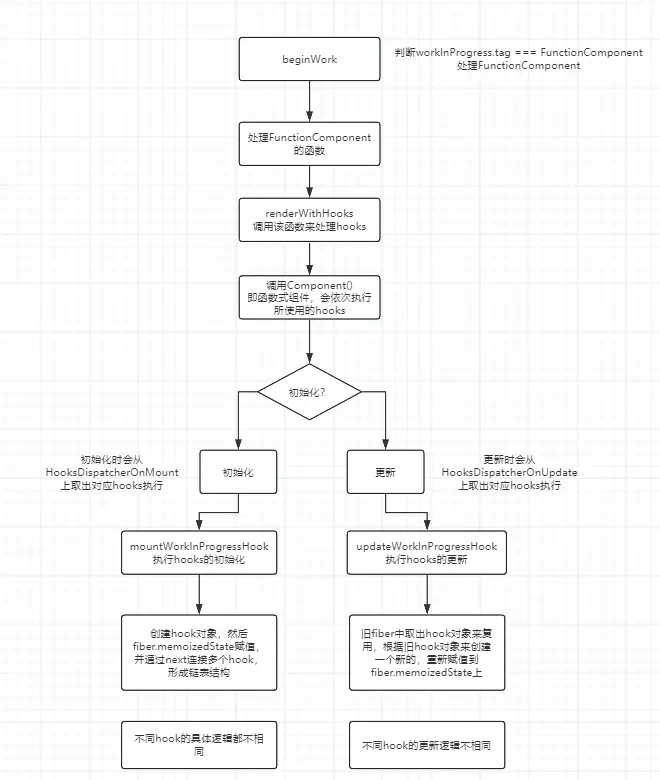
在beginWork中,遇到FunctionComponent会触发updateFunctionComponent函数,在该函数内执行renderWithHooks,是处理Hooks的入口。
// react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.js
function renderWithHooks(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
Component: (p: Props, arg: SecondArg) => any,
props: Props,
secondArg: SecondArg,
nextRenderLanes: Lanes,
) {
// workInProgress是当前正在reconciler的fiber节点,将这个节点放到currentlyRenderingFiber全局变量里面
currentlyRenderingFiber = workInProgress;
// 省略dev环境的处理
// 存hooks链表
workInProgress.memoizedState = null;
// 存放effect list 在commit阶段遍历这个
workInProgress.updateQueue = null;
workInProgress.lanes = NoLanes;
// 判断是初始化还是更新,选择不同的Hooks对象 HooksDispatcherOnMount HooksDispatcherOnUpdate
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =
current === null || current.memoizedState === null
? HooksDispatcherOnMount
: HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
// 执行Function Component,即我们写的函数组件。就会依次执行hooks
let children = Component(props, secondArg);
// 结束之后的一些处理
finishRenderingHooks(current, workInProgress, Component);
}可以看到,根据阶段的不同选择不同的Hooks对象:
- 初始化
HooksDispatcherOnMount - 更新
HooksDispatcherOnUpdate
初始化
在初始化时将ReactCurrentDispatcher.current全局变量赋值为HooksDispatcherOnMount对象。
在执行Component时会依次执行hooks时,会从ReactCurrentDispatcher.current中取出对应的hook来执行。
// HooksDispatcherOnMount
const HooksDispatcherOnMount: Dispatcher = {
useEffect: mountEffect,
useMemo: mountMemo,
useRef: mountRef,
useState: mountState,
// ...
};比如执行useStatehook,就会从这个对象上找到mountState来执行。
hook的初始化逻辑如下:
// react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.js
function mountWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
// Hook的结构
const hook: Hook = {
/*存hook的信息*/
memoizedState: null,
baseState: null,
baseQueue: null,
queue: null,
/** 通过next形成链表结构 */
next: null,
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// 之前没有hook 现在要新建一个hook
// currentlyRenderingFiber是当前的fiber节点, 将hook挂载到fiber的memoizedState上
// This is the first hook in the list
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook;
} else {
// 有多个hook 通过next指针来连接
// Append to the end of the list
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}- 将hooks信息存到
fiber.memoizedState上,通过next形成单向链表 - 通过
hook.memoizedState来存储不同hook需要的信息,比如useRef,存的就是{current: initialState}
更新
函数式组件重渲染的时候,会将ReactCurrentDispatcher.current赋值为HooksDispatcherOnUpdate,和初始化一样的逻辑,会从该对象上取出对应的hook来执行。
复用逻辑如下:
function updateWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
let nextCurrentHook: null | Hook;
if (currentHook === null) {
// alternate指向currentFiber中的节点 即旧的fiber节点
const current = currentlyRenderingFiber.alternate;
if (current !== null) {
// hooks链表第一个 复用旧的
nextCurrentHook = current.memoizedState;
} else {
nextCurrentHook = null;
}
} else {
// hooks链表非一个 直接通过next遍历旧的
nextCurrentHook = currentHook.next;
}
// 这个变量是当前fiber上的hook
let nextWorkInProgressHook: null | Hook;
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
nextWorkInProgressHook = currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState;
} else {
nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next;
}
if (nextWorkInProgressHook !== null) {
workInProgressHook = nextWorkInProgressHook;
nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next;
currentHook = nextCurrentHook;
} else {
// Clone from the current hook.
currentHook = nextCurrentHook;
const newHook: Hook = {
memoizedState: currentHook.memoizedState,
baseState: currentHook.baseState,
baseQueue: currentHook.baseQueue,
queue: currentHook.queue,
next: null,
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// This is the first hook in the list.
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = newHook;
} else {
// Append to the end of the list.
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = newHook;
}
}
return workInProgressHook;
}可以看到每次重新渲染时,会从旧的fiber节点中取出对应的hooks信息fiber.memoizedState来复用,复用逻辑和初始化时是一样的。
hook之所以不能写在判断语句中,因为每次重渲染都会从上一次fiber中取出hooks信息(
fiber.memoizedState),每次重渲染条件不会完全相同,在dev环境下,会判断两次渲染的hooks名称是否能对应,对应不上就会报错。源码中存有一个上一次hooks的名称数组
hookTypesDev,以及当前执行的hook名称currentHookNameInDev以及idx索引HookTypesUpdateIndexDev,hookTypesDev[hookTypesUpdateIndexDev] !== currentHookNameInDev不相等就报错
具体hooks的初始化\更新逻辑会根据hooks类型进行区分处理
状态派发
通过useState\useReducer来实现函数式组件的状态
初始化
会从HooksDispatcherOnMount中取出对应的hook执行:
function mountState(
initialState,
) {
const hook = mountStateImpl(initialState);
const queue = hook.queue;
const dispatch = (dispatchSetState.bind(
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber,
queue,
));
queue.dispatch = dispatch;
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}mountStateImpl的逻辑:
function mountStateImpl(initialState) {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
if (typeof initialState === 'function') {
// 兼容useState(() => data)的写法
}
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
const queue = {
pending: null,
lanes: NoLanes,
dispatch: null,
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer,
lastRenderedState: (initialState),
};
hook.queue = queue;
return hook;
}执行了
mountWorkInProgressHook,在该函数中执行了hooks的初始化。然后更新hook对象
hook.memoizedState赋值为传入的initialState- 创建一个queue对象,挂载到
hook.queue上。该属性是用来批处理的
mountStateImpl执行完成之后,hook对象就算是初始化完成了。
然后通过dispatchSetState.bind分发出一个dispatch更新函数,并且传入了fiber,这样就可以知道更新的fiber节点在哪里。
然后执行dispatch更新函数时:
function dispatchSetState(fiber, queue, action) {
const update: {
lane, action, next: null, // ...其他一些属性
}
if(isRenderPhaseUpdate(fiber)){
// 判断当前fiber处于渲染更新阶段 说明已经在更新了 那么不需要更新
const pending = queue.pending
if(queue.pending === null) {
update.next = update
}else {
update.next = pending.next
pending.next = update
}
queue.pending = update
}else {
// 不在渲染更新阶段
// ...
// 当前不在更新阶段,所以渲染更新
scheduleUpdateOnFiber()
}
}渲染更新阶段jsxexport default () => { const [count, setCount] = useState(1) const add = () => { setCount(d => d + 1) } }非渲染更新阶段jsxexport default () => { const [count, setCount] = useState(1) const add = () => { setTimeout(() => { setCount(d => d + 1) }, 100) } }
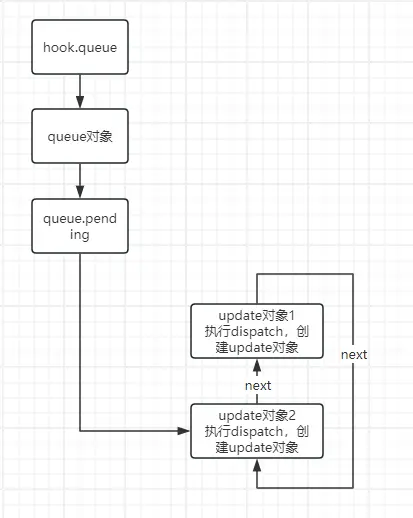
渲染更新阶段执行了dispath,会形成一个环状链表
export default () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(1)
setCount(d => d + 1)
setCount(d => d + 1)
}
非渲染更新阶段执行了dispath,做了以下事情:
- 判断当前state和上一次render时的state是否相等(浅比较)
- 不相等 执行
scheduleUpdateOnFiber执行更新
最后将更新函数dispatch放到queue.dispatch上。
更新
函数组件重新渲染时,会从HooksDispatcherOnUpdate上取出对应hook来执行,如updateState,会进入updateWorkInProgressHook函数,处理hook,然后调用updateReducerImpl。更新时useState、useReducer逻辑是一样的:
function updateReducerImpl(hook, current, reducer) {
const queue = hook.queue
const dispatch = queue.dispatch
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch]
}如果hook.queue.pending有值的话,更新流程如下:
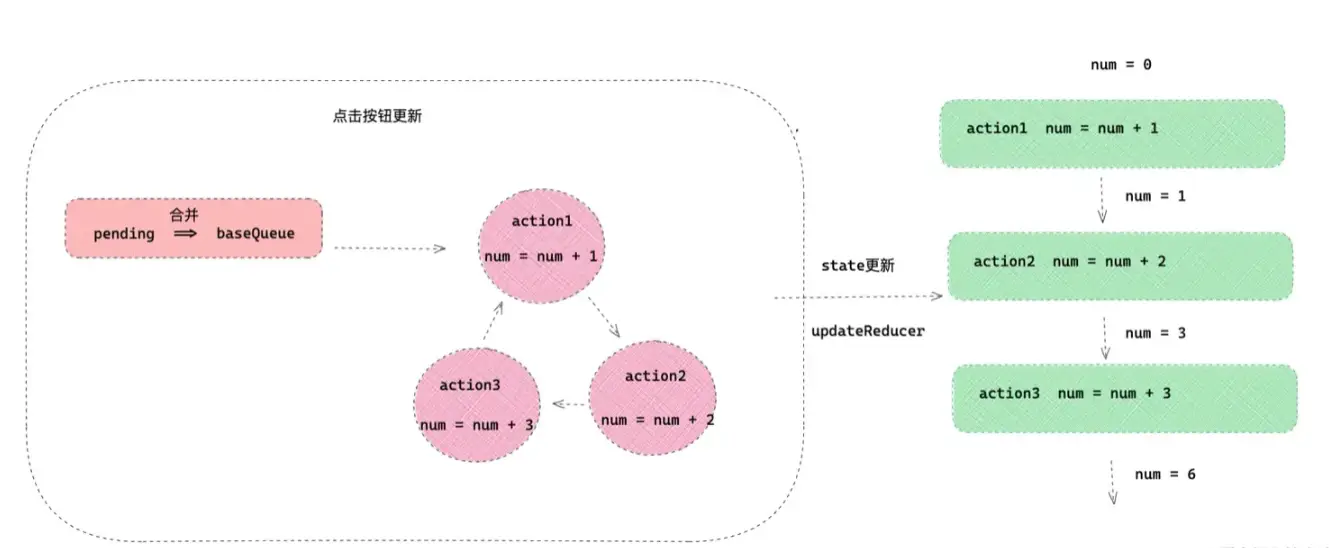
- 把待更新的
pending合并到baseQueue,然后循环更新。
useEffect 副作用
在render阶段,并没有操作DOM元素,而是将这些操作转成effectTag,等到commit阶段再同意处理这些副作用,这里的副作用包括useEffect\useLayoutEffect。
初始化
function mountEffect() {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook()
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
HookHasEffect | hookFlags,
create,
createEffectInstance(),
nextDeps,
);
}- 通过
mountWorkInProgressHook拿到hook - 通过
pushEffect创建一个effect,并保存到hook.memoizedState上- 在
pushEffect中创建了effect对象,而且如果有多个effect 还会形成链表,挂到fiber.updateQueue上
- 在
// effect对象结构
const effect = {
tag, create, deps, next
}- tag就是副作用的tag
- create是函数
- deps是依赖
- next是指针,形成链表
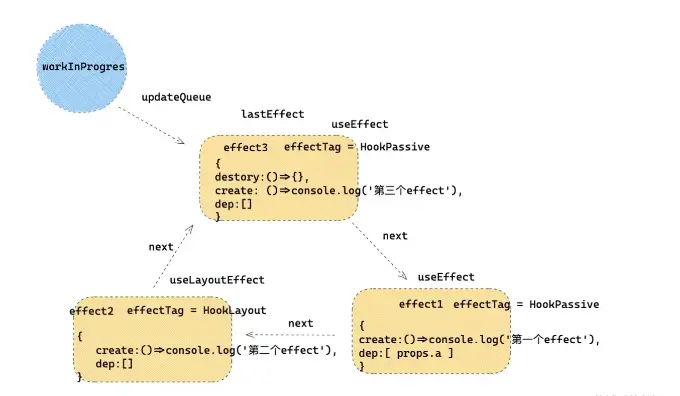
如果有以下代码:
React.useEffect(()=>{
console.log('第一个effect')
},[ props.a ])
React.useLayoutEffect(()=>{
console.log('第二个effect')
},[])
React.useEffect(()=>{
console.log('第三个effect')
return () => {}
},[])
更新
更新的核心逻辑就是判断deps有没有变化,如果没有变化,更新副作用链表。如果变化了,在更新副作用链表的同时,还会添加副作用tagcurrentlyRenderingFiber.effectTag = fiberEffectTag。
在commit阶段根据这effectTag来执行副作用。
effectTag
React中会使用不同的EffectTag来标记副作用,useEffect UpdateEffect|PassiveEffect,useLayoutEffect HookLayout。
然后在commit阶段根据不同的标识符来处理useEffect\useLayoutEffect的副作用。
useRef 状态获取
这就比较简单了,首先初始化时:
function mountRef() {
const ref = { current: initialValue }
hook.memoized = ref
return ref
}然后在更新时:
function updateRef() {
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook()
return hook.memoizedState
}就是将ref数据挂到hook.memoizedState上,更新的时候返回最新的就可以。
useMemo 缓存数据
初始化时:
function mountMemo(nextCreate,deps) {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook()
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps
const nextValue = nextCreate()
hook.memoziedState = [nextValue, nextDeps]
return nextValue
}在组件更新时:
function updateMemo(nextCreate,deps) {
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook()
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps
const prevState = hook.memoizedState
if(nextDeps !== null) {
const prevDeps = prevState[1]
if(areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps)) {
return prevState[0]
}
}
const nextValue = nextCreate()
hook.memoziedState = [nextValue, nextDeps]
return nextValue
}可以看到在组件更新时,会判断依赖是否发生了变化,没有变化直接返回上一次的缓存值。如果没有依赖或者是依赖变化了,会重新执行useMemo接受的函数生成一个新的值返回出去。
总结
reactHooks的核心原理就是闭包,将需要的信息放到fiber.memoizedState上保存,每次组件重新渲染,都会从旧的fiber节点中取出上一次的hooks信息重新创建。不同的hook实现的原理不同。
比较简单的useRef\useMemo等,就是闭包处理,初始化时创建对象,重渲染时取出对象。
比较复杂的useState\useEffect等,重渲染时除了需要拿到最新值,还需要处理一些其他的事情,比如effect副作用的处理。